
Net Metering Pakistan
Electricity demand in Pakistan has reached its highest level, while the energy supply is insufficient to meet people’s needs. The gap between energy demand and supply is growing over time. Electricity tariffs are consistently rising, and the resulting bills have a significant impact on people’s per capita income. There are several reasons why people are shifting towards solar energy from grid energy. However, a new issue emerged: how consumers can use solar energy at night or during periods of low sunshine. Solar consumers began to consider generating extra energy from solar panels to offset compensation policies through net and gross Metering.
The government supports solar consumers in different ways to achieve the country’s clean and green energy objectives.
What Is Net Metering?
People are investing millions of rupees in solar panel systems to minimize their reliance on grid electricity and lower their electricity bills. Net Metering policy is one of the primary reasons behind these investments. The government introduced a net metering mechanism that encourages solar energy consumers. The net metering concept is one of the government-promoting methods introduced by NEPRA in 2015. Through net metering regulations, Nepra allows electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOs) to buy excess electricity units from consumers and subtract them from units consumed from the grid.
Net Metering is a billing technique that permits the public to generate electricity through solar panels and contribute to the grid. Through net Metering, homeowners and businesses receive credits for surplus electricity generated by their solar panels.
According to government policy, people with a three-phase connection to hybrid and on-grid systems can use a net metering facility.
Net Metering Process In Pakistan
When Solar Panel Brands in Pakistan produce more energy than needed, the extra power is pushed to the grid, and based on this excess energy, the owners of solar systems receive credits. These credits can be used in the evening, at night, or when panels produce less electricity than needed.
Here is the net metering process explained through steps. For procedure guidance, an image of how net metering works is attached.
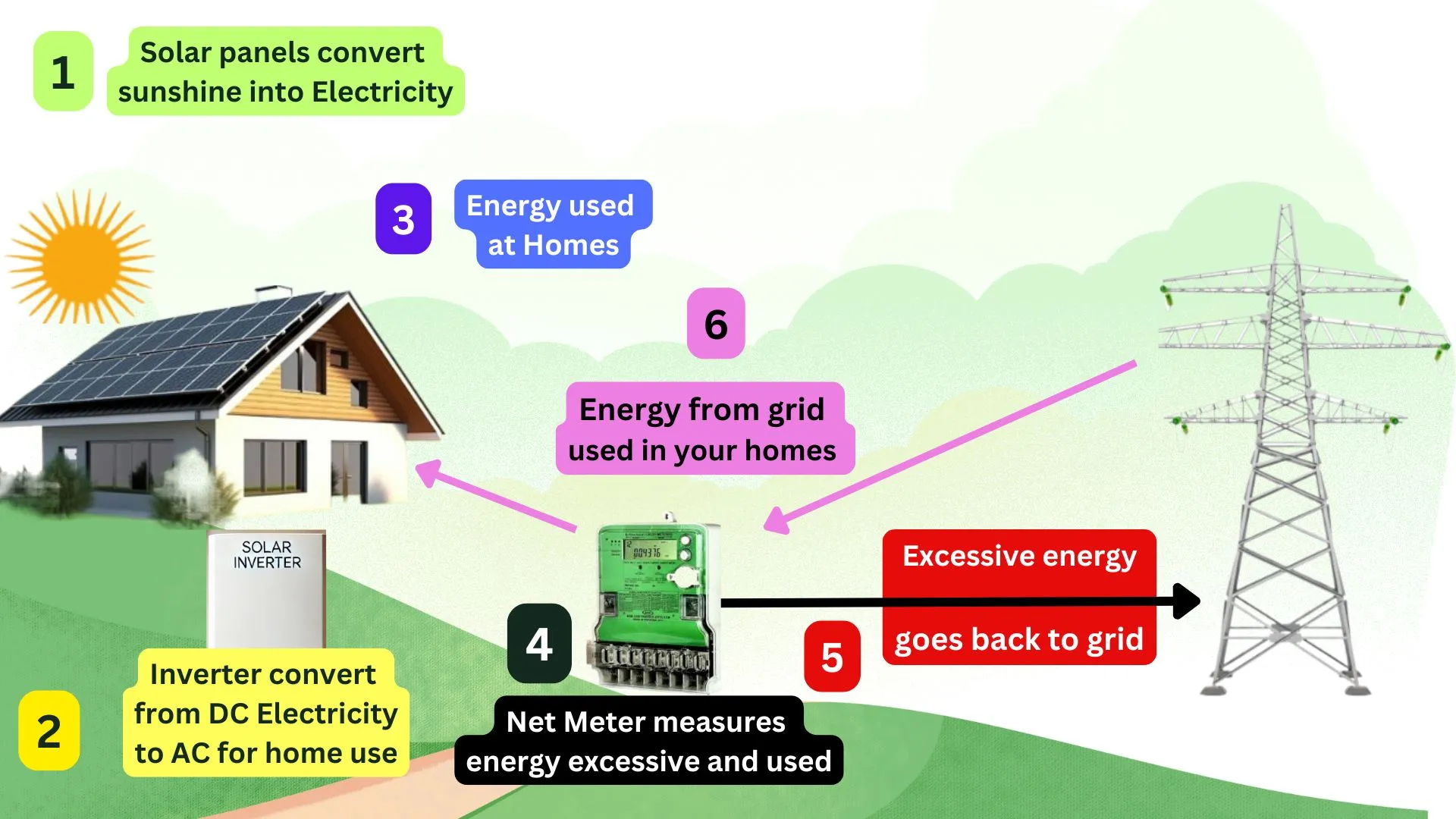
How can I apply for Net Metering?
Applying for net metering in Pakistan is a simple process regulated by NEPRA. Homeowners or businesses with a solar system can apply through their local electricity distribution company (DISCO), such as LESCO, MEPCO, IESCO, HESCO, or K-Electric. Before applying, make sure you have all the required documents ready, including your CNIC, the latest electricity bill, system layout, panel and inverter datasheets, and your installer’s certification. After submission, the DISCO team conducts a technical inspection to ensure your solar setup meets safety and quality standards. Once approved, a bi-directional (net) meter is installed that measures both imported and exported electricity. The extra energy you send to the grid will be credited to your monthly electricity bill.
The steps involved in the net-metering application, as per Nepra’s regulation rules, will guide consumers in obtaining an authorized license and distribution facility.
Step 1
Submit Application
Any applicant who meets the requirements of DG can submit an application with the required documents to the related DISCO as defined in the Nepra regulations.
Step 2
Application Acknowledgement
Within five working days, DISCO will acknowledge receipt of the application and inform the applicant whether it’s complete or if anything is missing in the application.
Step 3
Initial Review
After receipt of an application, twenty working days will be required for initial review. In this review, DISCO will determine the qualifications of the applicant.
Step 4
Technical feasibility
If the proposed facility is found technically infeasible in the initial review, DISCO will return the application to the applicant within three working days.
Step 5
Agreement Signing
If the DISCO office is satisfied with the applicant’s qualification as a DG, then the applicant and DISCO will sign the agreement within ten working days after review.
Step 6
Generation Licence
The DISCO office will send a copy of the agreement with the application to Nepra for a generation license within seven working days of signing the contract.
Step 7
Connection Charge Estimate
DISCO will issue the CCE after agreement on the required modification of the network. The applicant will receive a connection charge estimate for the proposed facility.
Step 8
Payment of CCE
The applicant will deposit the CCE (connection charge estimate) into the related bank within twenty days of issuance and inform the DISCO office in writing about payments.
Step 9
Installation Facility
After the payments, the DISCO office will install and commission the proposed facility within thirty working days, following confirmation of the license by Nepra to DG.
License Fee Structure For Net Metering
NEPRA regulates the license fee structure for net Metering in Pakistan and varies depending on the system’s capacity. Generally, small-scale domestic solar systems up to 25 kW have a minimal or no license fee, while larger commercial or industrial systems may require a small processing or registration fee. These charges help cover administrative and inspection costs. The fee is usually paid once during the application process before the license is issued.
Size Of System | Application Fee |
0-20 KW | Free |
20-50 KW | 5,00 PKR |
50-100 KW | 1,000 PKR |
100-1000 KW | 5,000 PKR |
Distribution Companies In Pakistan (DISCOs)
Distribution companies in Pakistan, commonly known as DISCOs, are responsible for supplying electricity to consumers across various regions of the country. These companies operate under the supervision of the National Electric Power Regulatory Authority (NEPRA) and are essential for maintaining the power distribution network. Each DISCO serves a specific geographic area, ensuring the delivery of electricity from the national grid to homes, industries, and businesses. Below is the list of major electricity distribution companies operating in different cities and regions of Pakistan:
Net Metering Price In Pakistan
Net metering costs in Pakistan vary based on area, solar project size, and installation equipment. Here is the price breakdown structure for net metering installation in Pakistan.
Solar Panel cost in Pakistan
The cost of a solar panel system depends on the total kilowatt capacity you want to install—for example, 3 kW, 5kw, or 10 kW.
Green Meter price in Pakistan
A green meter or net meter is a device that needs to be installed to measure electricity consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The green meter records both sides of electricity: electricity consumed by consumers and electricity generated by solar panel systems.
Nepra will approve the green meter once solar consumers have accepted the application.
The price of the green meter in Pakistan is 39,000 PKR.
Net Metering application fees.
The net metering application fee is 5,000 to 10,000 PKR based on KW.
Cost of inspection and approval
The cost of inspection and NEPRA approval is 10,000 to 20,0000 PKR.
Additional costs
Location, area, warranty, weather, and quality can affect cost.
Difference Between Net Metering and Green Metering
With the rapid adoption of solar power in Pakistan, selecting the proper electricity meter has become a crucial step. Two terms often confuse homeowners and businesses: Net Meter and Green Meter. Although both meters are used for monitoring electricity consumption and generation, their purposes and features differ. This article explains what each meter does, its price difference, and which one may be better for you.
What Is Neter Meter?
A net meter is a bi-directional electricity meter used under Pakistan’s net metering policy. It measures:
- Electricity is imported from the national grid.
- Electricity is exported from your solar power system to the grid.
When your solar system generates extra electricity, the net meter records the exported units. During times when your solar generation is low (like at night), electricity is imported from the grid. At the end of the month, your electricity bill is calculated based on the net difference between imported and exported units.
What is a Green Meter?
A Green meter is an advanced version of a standard electricity meter. It is also known as a smart meter because it can be read remotely and offers more detailed energy monitoring.
Neter Meter | Green Meter |
Bi-directional measurement (import/export) | Provides real-time electricity usage and Smart energy monitoring & theft detection |
Required for official net metering approval by NEPRA and local DISCO | Designed to support innovative grid projects and future energy systems. |
Commonly installed in homes and businesses using solar panels | Can be monitored remotely, reducing the need for physical meter reading. |
Basic bi-directional meter | Advanced smart meter with remote monitoring |
A Green Meter Price in Pakistan is almost 30,000 PKR | A Green Meter Price in Pakistan is nearly 40,000 PKR |
Standard System Today | May replace the net meter in the future |
What Is Gross Metering?
The number of solar panel consumers is increasing regularly due to Pakistan’s energy shortage. However, solar consumers are concerned about nighttime issues and are seeking solutions to address this problem. Similar to net Metering, Gross Metering is a billing compensation technique available to solar customers, albeit with a different methodology. In gross Metering, solar consumers sell all produced electricity to the grid at lower rates and buy electricity from the grid at higher rates for home use.
As explained, in net Metering, solar panel users can send extra energy generated at home to the grid and take it back from the grid in equal amounts. However, in gross Metering, consumers send all their solar panel-generated energy to the grid at government rates and use grid energy according to electricity bills.
Difference Between Net Metering And Gross Metering
Gross Metering and net metering serve similar purposes in saving extra electricity units produced by solar panels, but they differ in policy and procedure. Here is the key difference between net metering and gross metering through an example.
In Net Metering | In Gross Metering |
For example, if you generate 20 units from the solar panels during the daytime, you use 10 units while sending the remaining 10 units to the grid. | For example, if you produce 20 units from the solar panels during the daytime, you will send all 20 units to the grid without any consumption. |
Same retail rates of buying and selling (receive credits and reduce bills) | All the electricity units go to the grid at different rates and are bought from the grid at different rates. |
Consumers separate first and then send extra energy to the grid | Solar panels can not provide solar energy to homes directly. |
The Green Meter records all send and receive | The meter records how much is generated |
Bill will reflect only net billing (the difference between energy used and sent) | Separate billing for send and back |
Best for Business and residential | Best for commercial and industrial |
What is MCO in Metering?
MCO stands for meter change order. When electricity consumers request DISCO to replace or change their electricity meters due to reasons such as being faulty, damaged, or stolen, they need an MCO (Meter Change Order). Net meetings are also important because they enable people to convert their current normal meter into a gross or net meter. For this transaction, consumers need an MCO from the respective authorities in Pakistan.
Conclusions
The primary goal of installing solar panels in Pakistan is to reduce reliance on grid electricity and lower energy bills. The cost of electricity is not affordable for many people, and in most areas, electricity remains absent for many hours a day. The other purpose is to save spare electricity for the night. The night issue remains the same in accommodations because solar panels can be helpful during the day.
Solar energy consumers are finding the best ways to resolve this issue, especially in winter, when night and low sunshine time for up to 12 hours.
In Pakistan, net Metering is a better solution than gross Metering. In gross Metering, people will have to pay the same higher electricity tariffs against consuming electricity from the grid. Electricity tariffs in Pakistan are very high. If the government plans to shift the net metering policy to gross Metering, it would be a very discouraging move for solar panel consumers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Net Metering
What is net metering?
Net Metering is a billing technique that permits the public to generate electricity through solar panels and contribute to the grid. Through net metering regulations, Nepra allows electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOs) to buy excess electricity units from consumers and subtract them from units consumed from the grid. According to government policy, people with a three-phase connection to hybrid and on-grid systems can use a net metering facility.
What is the new net metering policy in Pakistan 2025?
The proposed new policy plans to replace net metering with gross metering (or net billing) for new solar users. Instead of offsetting your electricity bill, you will sell all generated electricity to the grid at a reduced buy-back rate (10–11.33 PKR per unit), while buying electricity separately from WAPDA at full price, which is approximately 33-37 PKR per unit. So, units sold will be almost one-third of the buying amount per unit.
Whereas, existing users will not be affected and will continue to receive 27 PKR per unit under the current net metering Policy.
What is the latest news about net metering in Pakistan?
As of July 2025, the government is reviewing public and industry feedback before finalizing the new policy. NEPRA has not yet approved the policy. While no official implementation date has been announced, discussions are active, and the gross metering model may soon be enforced for new connections only.
Is the government ending the net metering Policy?
No, the government is not ending net metering for existing users. However, a new policy is being considered for new users, where net metering may be replaced with gross metering or net billing. Under this, you sell all generated electricity at a lower rate (10–11.33 PKR per unit) instead of offsetting your usage. However, new users can also mitigate this issue by increasing the number of solar panels.
What is the minimum solar system size required for net metering?
To apply for net metering in Pakistan, your solar system must be at least 3 kW in size. However, some DISCOs prefer or approve applications starting from 5 kW or above for smoother processing.

This site helped me download my duplicate Lesco bill right before due date. Super helpful and hassle-free!
Somebody necessarily lend a hand to make significantly articles I’d state. This is the very first time I frequented your web page and so far? I amazed with the analysis you made to create this particular post extraordinary. Great task!
This information on net metering is very useful for Pakistani consumers. For anyone managing their household utility expenses, a major headache occurs when the SNGPL, SSGC, or DISCO bill is not showing up online to check consumption or make payments. We’ve compiled a quick, straightforward guide to help users troubleshoot and resolve this digital billing error.